100%
Protection
1400+
Monitored machines
seamless
Integration
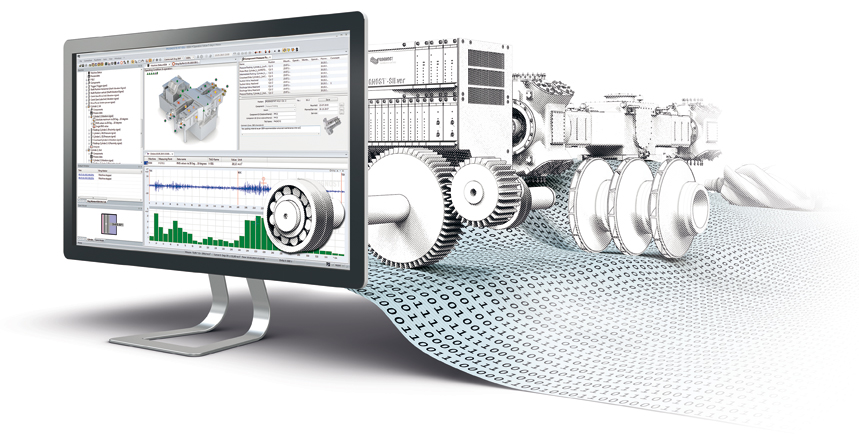
Our support provides the seamless integration of our systems in your plant
professional
approach
Continuous integration of user requirements and practical experience
client-centric
Focus
Customer-specific design, installation and individual commissioning
sustainable
Growth
More users show that our importance in the market increases constantly
client
testimonials
“PROGNOST is what it takes to have full compressor transparency.”
Ricardo Franco, Maintenance, BRASKEM, Brasilien
It All Starts With a consultation!
For any kind of quiries, Please call
Daimlerstraße 10, 48432 Rheine, Germany